Satellite Camp Redl-Zipf
Establishment of the satellite camp
In September 1943, the decision was made to house the operation of the missiles production for the German Reich in the seized cellars of the beer brewery in Zipf. Special facilities were built to test engines for Aggregate 4, the so-called “miracle weapon” V2, and to produce liquid oxygen for fuel. To conceal the facilities, the bunkers in Zipf were covered with nets and all buildings were sprayed black. The code name of this arms production facility was “Steinbruch-Verwertungs GmbH, Betrieb Schlier” (quarry exploitation) - or, short, “Schlier” , named after the marl deposits in Zipf. Already in October 1943, the SS transferred the first prisoners to Zipf to start setting up Redl-Zipf Subcamp. On 11 October 1943, Schlier-Redl-Zipf Subcamp was officially established. It was also referred to as “Rella X”.
Location
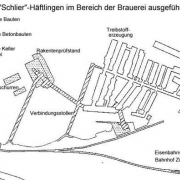
The camp was located near the works premises and was made up out of four accommodation barracks and one kitchen barrack.
Prisoners
The first prisoners arrived at Sclhlier-Redl-Zipf Subcamp in October 1943, supervised by SS-Hauptsturmführer (Chief Assault Leader) Georg Bachmayr, and were assigned to set up the camp. By winter of 1943, approx. 1,500 prisoners were detained there. The number of prisoners varied considerably; the highest number was reached in December 1943, with around 1,900 people. The majority of the prisoners were from France, Italy, Poland, the Soviet Union, and Spain. The living and working conditions on site claimed many lives. In total, at least 267 prisoners died at Redl-Zipf Subcamp. Numerous accidents also happened during the production of the liquid oxygen. After an explosion, prisoners were suspected to have attempted sabotage.
Forced labor
The prisoners had to work on the expansion and conversion of the mentioned brewery cellar, on the construction of a bunker to house the test facilities for rocket combustion chambers, on the construction of a transformer bunker, and on the construction of a railway feeder line. Phone lines and power cables were laid, and a wastewater treatment plant was built. After the facility was completed (after several delays), the remaining prisoners were used for maintenance work. The day shift started at 7 a.m. and lasted 12 hours; at 7 p.m., shift change occurred. The night shift then lasted until 7 a.m. the next morning. They had to work in all weathers, without any days off. Prisoners who had become unable to work were transferred back to Mauthausen. In April 1945, the so-called “Unternehmen Bernhard”, which worked on document falsification and counterfeiting, moved to Zipf for several weeks. 142 prisoners were transferred to Schlier-Redl-Zipf Subcamp via Mauthausen from Sachsenhausen Concentration Camp. They were assigned to resume the counterfeiting work. However, the production of counterfeit banknotes never actually started in Redl-Zipf (counterfeit dollar bills were planned for May 1945). Before the evacuation to Ebensee Subcamp, boxes full of counterfeit money with faults were burned in a forest in the area.
Guarding
The subcamp was guarded by Wehrmacht and SS units. SS-Hauptsturmführer (Chief Assault Leader) Georg Bachmayer was first camp leader. SS-Obersturmführer (Senior Assault Leader) Alfons Bendele (or Bentele) replaced camp commander Karl Schöperle and was the last camp commander of Schlier-Redl-Zipf Subcamp.
Closure
On 3 May 1945, the prisoners were brought to Ebensee either on foot or loaded on trucks. The next day, the SS shut down the camp, burned it to the ground, and made the prisoners help cover any traces. On 6 May, US Soldiers liberated the prisoners of Ebensee Subcamp.
Commemoration and remembrance
Any remains of the former camp can no longer be found. Zipfer Brewery only allows limited access to the tunnel system. Upon initiative of former prisoners, a monument was erected near the church in Zipf in 1985, and it was amended in 2014. The Mauthausen Committee Vöcklabruck [2] and the ARGE Schlier [3] organise an annual memorial celebration. The date for it can be found in the programme for commemoration and liberation celebrations [4].